Tax obligations in Antigua and Barbuda are straightforward: residents pay no personal income tax, corporations pay a standard 25% rate, and the country offers significant tax benefits. This system applies to both local and international income, with specific provisions for different business types and residency statuses. Most notably, IBCs pay 0% corporate tax for activities outside the territory, making company formation in Antigua and Barbuda highly attractive in terms of tax liability. This guide details the specific fiscal responsibilities for businesses, including the comprehensive ABST consumption tax and payroll levies.
Key Takeaways On Tax and Accounting Requirements in Antigua and Barbuda
| What Are The Accounting Standards in Antigua and Barbuda? | Businesses must register with the Inland Revenue Department and file tax returns if their annual sales exceed EC$300,000. U.S. citizens in Antigua must comply with FATCA. This act requires them to report accounts, assets, and foreign investments, keeping them accountable to the IRS. |
| What is the corporate income tax rate for businesses? | Corporate taxation in Antigua and Barbuda operates on a flat 25% rate for income earned locally, with banks qualifying for a 22.5% rate when offering low-interest mortgages, and specific sectors like insurance enjoying a preferential 10% rate. An International Business Company (IBC) benefits from a special tax regime. International Business Corporations in Antigua and Barbuda enjoy a 0% corporate tax rate and complete confidentiality protection, making them highly advantageous for international investors. |
| The Antigua and Barbuda Sales Tax (ABST) is a value-added tax set at 15%. | The standard VAT rate is 15% for goods and services, with a reduced rate of 14% for hotels and some other services as well as exemptions for essential goods. |
| Dividend Tax Rate in Antigua and Barbuda | 0% on dividends paid to residents. Non-residents, however, face a 12.5% withholding tax on dividends, interest, and royalties. |
| What is the deadline for filing the annual corporate income tax return? | Annual returns are due by March 31st of the following year, with final payments required by April 30th. |
| Why set up an IBC? | IBCs are granted significant tax concessions. |
Key Terms
- ABST: Antigua and Barbuda Sales Tax
- TIN: Tax Identification Number
- IBC: International Business Corporation
- DTC: Double Taxation Convention
- TIEA: Tax Information Exchange Agreement
- CBI: Citizenship by Investment
Key Business Taxes in Antigua and Barbuda
1. Corporate Income Tax (CIT)
The standard corporate tax rate in Antigua and Barbuda is 25%, with special rates of 22.5% for qualifying banks and 10% for insurance, oil, and telecommunications companies.
This tax is levied at a rate of 25% on the taxable income of a company. Businesses are required to file an annual CIT return by March 31st of the following year.
2. Antigua and Barbuda Sales Tax (ABST)
This is a 15% value-added tax applied to most goods and services. Registered businesses must charge ABST, collect it from customers, and remit the net amount (collections minus credits) to the IRD on a monthly basis.
Expert Tip: Strict ABST Filing Deadlines
From our experience, the Inland Revenue Department is particularly strict regarding the Antigua and Barbuda Sales Tax (ABST). This is a VAT-style tax of 15%. Returns must be filed and paid by the end of the calendar month following the tax period.
Late filing attracts immediate penalties of 5% per month plus interest. Unlike annual taxes where extensions might be possible, ABST deadlines are rigid. We advise clients to implement a robust monthly accounting close process to ensure ABST figures are ready well before the deadline.
3. Withholding Tax
Payments made to non-residents for services like royalties, interest, and management fees are subject to a withholding tax, typically at a rate of 25%. This tax must be withheld by the paying company and remitted to the IRD.
4. Social Security and Other Contributions
Employers must deduct contributions from employees’ salaries and make their own contributions for social security, medical benefits, and an education levy.
Advantages for International Business Corporations (IBCs)
International Business Corporations in Antigua and Barbuda enjoy a 0% corporate tax rate and complete confidentiality protection, making them highly advantageous for international investors.
Filing Requirements for Businesses
Businesses must register with the Inland Revenue Department and file tax returns if their annual sales exceed EC$300,000. Annual returns are due by March 31st of the following year, with final payments required by April 30th. Quarterly remittances are due on April 15th, July 15th, October 15th, and January 15th. Late filing incurs penalties of either $500 or 5% of tax due per month (whichever is greater), plus 20% of unpaid tax and 1% monthly interest on outstanding balances.
Personal Income Tax in Antigua and Barbuda
Since 2016, Antigua and Barbuda has maintained a zero personal income tax policy for its residents. This means citizens and residents pay no taxes on their worldwide income, with only locally-sourced income being subject to specific regulations.
In Antigua and Barbuda, personal income tax is nonexistent for residents and citizens. Non-residents, however, face a 12.5% withholding tax on dividends, interest, and royalties. Self-employed individuals need to know about different tax rates: 0%, 8%, or 25%. They must also register for an Antigua Tax Identification Number. Here’s a quick look at some key points:
- Residents: No personal income tax.
- Non-residents: 12.5% withholding tax on certain incomes.
- Self-employed: Tax rates of 0%, 8%, or 25%.
Additionally, residents do not pay taxes on dividends, royalties, interest, inheritance, wealth, or capital gains. However, social contributions and property taxes apply when dealing with real estate.
Deductions and Exemptions for Residents
Tax deductions and exemptions in Antigua and Barbuda primarily benefit businesses, offering tax-free status on certain income types for up to 20 years, along with specific deductions for income-generating expenses and customs duties exemptions.
Tax Residency Requirements
To qualify as a tax resident in Antigua and Barbuda, individuals must either maintain a minimum stay of 30 days per year or opt to pay an annual flat tax of USD 20,000. The application process takes approximately 2 months and requires comprehensive documentation including passport copies, bank references showing minimum annual income of USD 100,000, police clearance, and property ownership evidence.
Required documentation includes:
- Birth certificate copy
- Primary passport page copy
- Two passport-sized photographs
- Marriage certificate (if applicable)
- Police report covering past 2 years
- Bank reference and statement (minimum USD 100,000 annual income)
- Two character references (5+ years of acquaintance)
- Medical report
- Certificate of naturalization (if applicable)
- Property lease/title in Antigua and Barbuda
Tax Benefits for Residents and Expatriates
Antigua and Barbuda offers significant tax advantages to both residents and expatriates, including zero personal income tax, no capital gains tax, and no inheritance tax, creating an environment focused on wealth preservation.
Unique Tax Benefits for Residents
Tax residents in Antigua and Barbuda enjoy comprehensive tax exemptions on worldwide income, with additional benefits including no taxes on exports, domestic utilities, and various other activities.
Tax Incentives for Expatriates
Expatriates in Antigua and Barbuda can establish businesses without facing local taxes and benefit from simplified corporate tax structures, making it an attractive destination for international investors.
Residency vs. Non-residency Implications
The key difference between residency and non-residency status lies in taxation scope: residents enjoy tax-free status on worldwide income, while non-residents face a 25% withholding tax on local-source income including dividends, interest, and royalties.
Tax Considerations for American Expats
American expatriates in Antigua and Barbuda must balance their U.S. tax obligations with local tax benefits, as they remain subject to U.S. worldwide income reporting requirements despite the country’s zero personal income tax policy.
Tax Considerations for American Expats
American expats living in Antigua and Barbuda benefit from the lack of personal income taxes. This was abolished in April 2016, making it favorable for U.S. citizens. However, they must still report their worldwide income to the IRS. They have to meet U.S. tax obligations no matter where they live. In Antigua and Barbuda, the only personal tax is a transfer tax for gifts, which helps minimize their tax burdens.
Double Taxation Avoidance Treaties
Antigua and Barbuda maintains 12 Double Taxation Treaties (DTC) with countries including Barbados, Belize, and Sweden to prevent the double taxation of income.
Property Tax Obligations for U.S. Citizens
U.S. citizens who own property in Antigua and Barbuda must pay property tax. Rates range from 0.1% to 0.5%, based on the property’s value and location. The Property Tax Act No. 15 of 2000 lays out these rates. For non-resident owners of undeveloped land, the rates are higher, ranging from 10% to 20%. Additional costs, such as stamp duty and insurance fees, are applicable when purchasing property. The same rules apply to U.S. citizens as to other non-residents.
Reporting Requirements under FATCA
U.S. citizens in Antigua must comply with FATCA. This act requires them to report accounts, assets, and foreign investments, keeping them accountable to the IRS. Non-resident companies in Antigua aren’t taxed there, but owners must report to their home country. The IRS is strict about offshore accounts, and failing to report can result in fines. It’s wise to seek advice from a tax lawyer in Antigua for compliance. This helps avoid any legal trouble and ensures all assets are properly declared.
Tax Treaties and Avoidance Strategies

Antigua and Barbuda maintains 12 Double Taxation Treaties (DTCs) and 17 Tax Information Exchange Agreements (TIEAs). Key treaty partners include Barbados, Belize, Sweden, the United Kingdom, United States, and Australia. These agreements facilitate international business while ensuring tax compliance and transparency.
The country’s network of tax treaties helps prevent double taxation while maintaining transparency. DTCs cover key areas including:
- Income tax coordination
- Withholding tax reductions
- Profit repatriation provisions
- Capital gains treatment
- Exchange of tax information
Additionally, the 17 TIEAs with countries like Australia, Belgium, and the UK enhance international cooperation and compliance standards.
Strategies for tax avoidance and mitigation
There are many ways to reduce tax burdens while investing in Antigua and Barbuda. US citizens can use tax credits, like filing Form 1116 for a foreign tax credit, to lower taxes. Contributing to retirement accounts, such as IRAs or 401ks, can also decrease taxable income.
Donations to funds like the National Development Fund may provide deductions too. The tax-friendly environment excludes capital gains, estate, and personal income taxes, easing tax planning. However, there may be costs like stamp duty on property transfers. Thus, it’s crucial to plan carefully.
Key takeaways for effective tax planning
To make the most of Antigua and Barbuda’s tax system, consider a few key points. The corporate income tax is flat at 25%. Personal income tax isn’t required, offering better disposable income. A 5% stamp duty applies to real estate. There’s no gift tax, allowing easy wealth transfer without extra costs. Engaging a tax expert is vital to understand the complexities involved and avoid errors. These practices can help in achieving effective tax planning.
By using these treaties and strategies, individuals and businesses can efficiently manage their tax liabilities. Engaging with local regulations and opportunities is essential for effective planning. Whether through avoiding double taxation or leveraging local benefits, Antigua and Barbuda provides advantageous pathways for tax planning.
The Role of the Inland Revenue Department (IRD)
The Inland Revenue Department (IRD) is the primary government agency responsible for the administration and collection of taxes in Antigua and Barbuda. All companies must register with the IRD and are responsible for filing returns and remitting payments for all applicable taxes.
Recent Updates and Changes in Tax Law
As of 2024-2025, Antigua and Barbuda has implemented significant tax changes:
- ABST increase to 17% (12.5% for hotels, 10.5% for certain goods/services)
- Removal from EU non-cooperative jurisdictions list (October 2024)
- Pending OECD Global Forum review
- Maintained 25% corporate tax rate with 10% rate for qualifying sectors
Citizenship by Investment Program

Antigua and Barbuda’s Citizenship by Investment Program offers four investment options as of 2025:
- National Development Fund: USD$230,000
- Real Estate Investment: USD$300,000+
- University Fund: USD$260,000
- Business Investment: USD$1,500,000+
The program provides a path to citizenship with significant tax benefits, including access to the country’s favorable tax regime and visa-free travel to over 150 countries. Processing typically takes 5-7 months, with the following fees:
- Due diligence fees:
- Main applicant: USD$7,500
- Dependents over 18: USD$4,000
- Dependents 12-17: USD$2,000
- Processing fee: USD$30,000 (family up to 4)
- Additional dependent fee: USD$15,000 each
Tax Advantages of Citizenship by Investment
The program offers major tax benefits including:
- No personal income tax obligations
- Zero tax on capital gains
- No inheritance or wealth tax
- Access to International Business Corporation benefits
- Tax advantages in the Caribbean dollar economy
Eligibility and Application Process
To apply, candidates must meet specific criteria and follow these steps:
- Choose an authorized agent to guide the application
- Select an investment option
- Complete due diligence process
- Submit required documentation
- Make the investment
- Receive citizenship approval
This streamlined process makes acquiring citizenship in Antigua and Barbuda both appealing and straightforward.
Caribbean Tax Rate Comparison
Antigua and Barbuda’s tax structure remains competitive within the Caribbean region. The corporate tax rate of 25% matches Dominica’s rate and is lower than St. Kitts and Nevis (33%), St. Lucia (30%), and Grenada (28%). The country’s sales tax of 15% (14% for hotels) sits between St. Kitts and Nevis’s 13% and St. Lucia’s 12.5%.
FAQs When Understanding Accounting and Taxation in Antigua and Barbuda
Based on our experience these are the common questions and doubts of our clients.
The standard corporate income tax rate in Antigua and Barbuda is 25% on the company’s net profits.
The tax authority in Antigua and Barbuda is the Inland Revenue Department.
Businesses must register with the Inland Revenue Department and file tax returns if their annual sales exceed EC$300,000.
U.S. citizens in Antigua must comply with FATCA. This act requires them to report accounts, assets, and foreign investments, keeping them accountable to the IRS.
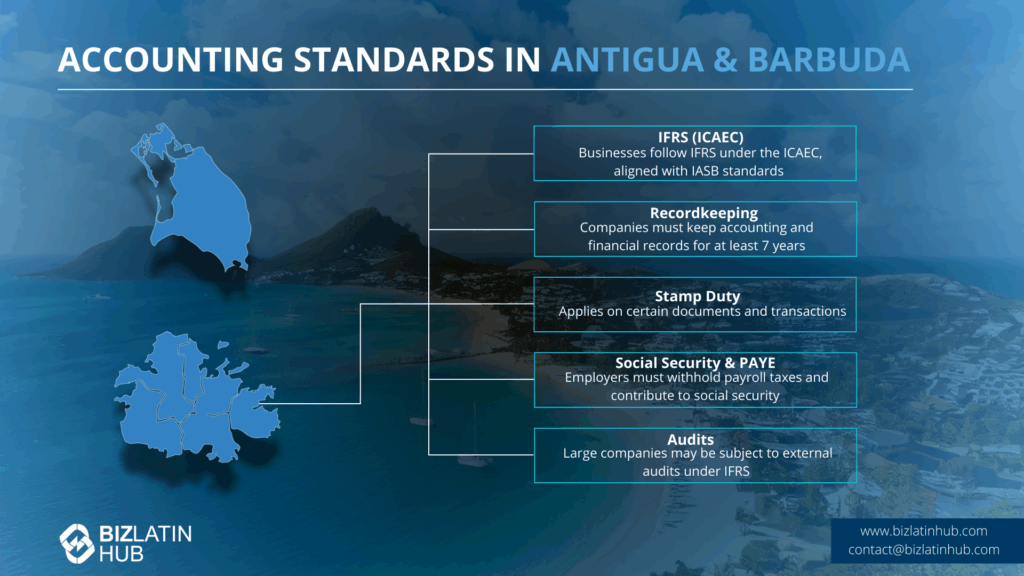
This is managed on the island by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of the Eastern Caribbean (ICAEC).
Essentially, yes. The ICAEC uses IFRS rules and follows IASB guidance when organizing its affairs.
ABST is a value-added tax charged on most goods and services supplied in Antigua and Barbuda. The standard rate is 15%. Businesses with annual sales exceeding ECD $300,000 must register for ABST.
Yes, investors can form an International Business Company (IBC), which is subject to a corporate tax rate of only 1% on its international profits. IBCs are also exempt from withholding taxes.
Employers must deduct and pay Social Security (6% employer, 4% employee), Medical Benefits (3.5% employer, 3.5% employee), and Education Levy.
The Unincorporated Business Tax (UBT) applies to sole traders and partnerships. It is charged on gross income (less certain deductions) at rates sliding from 0% to 25%.
Biz Latin Hub can help you manage your tax obligations in Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda offers significant opportunities for businesses, but staying compliant with local tax and accounting regulations is essential to your success.
Biz Latin Hub provides tailored tax and accounting services designed to meet the unique needs of businesses in Antigua and Barbuda. Our expert team can assist with bookkeeping, tax compliance, payroll management, and financial reporting, ensuring that your business operates efficiently and in full compliance with local laws.
Get Started Today
Contact us for more information. Response within 24 hours.






