The growing market for foreign investors looking at company formation in Jamaica is fueled by its strategic location, stable political environment, and well-established tourism industry. The government’s proactive measures to improve infrastructure and streamline business processes have contributed to the country’s attractiveness for international investments. However, tax and accounting requirements in Jamaica can be hard to understand at first.
Key takeaways
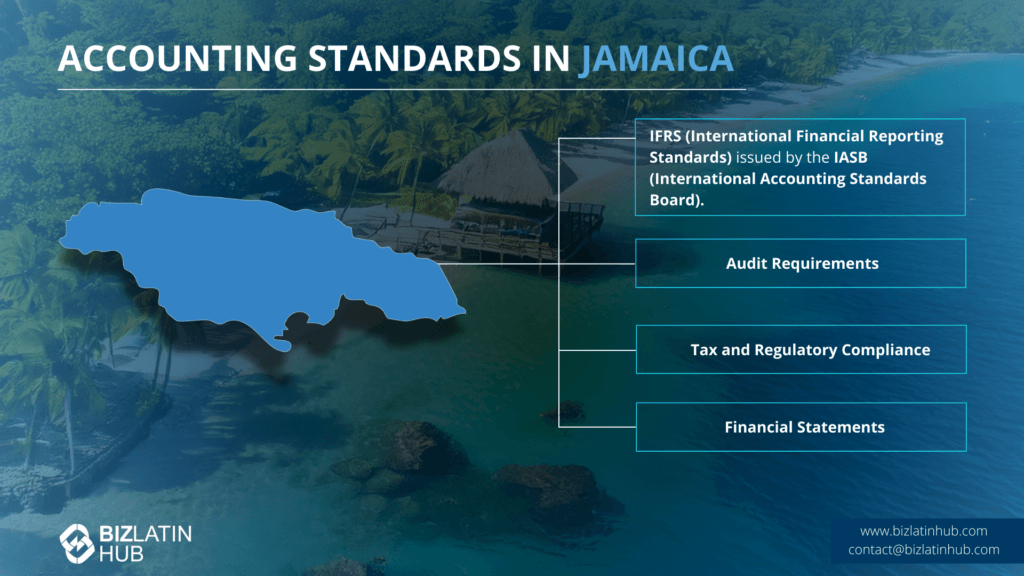
| What Are The Accounting Standards in Jamaica? | The Institute of Chartered Accountants of Jamaica (ICAJ) holds the authority granted by the Public Accountancy Act as the standard-setter in the jurisdiction. ICAJ has officially embraced and implemented IFRS and IFRS for SMEs as the prevailing accounting standards. |
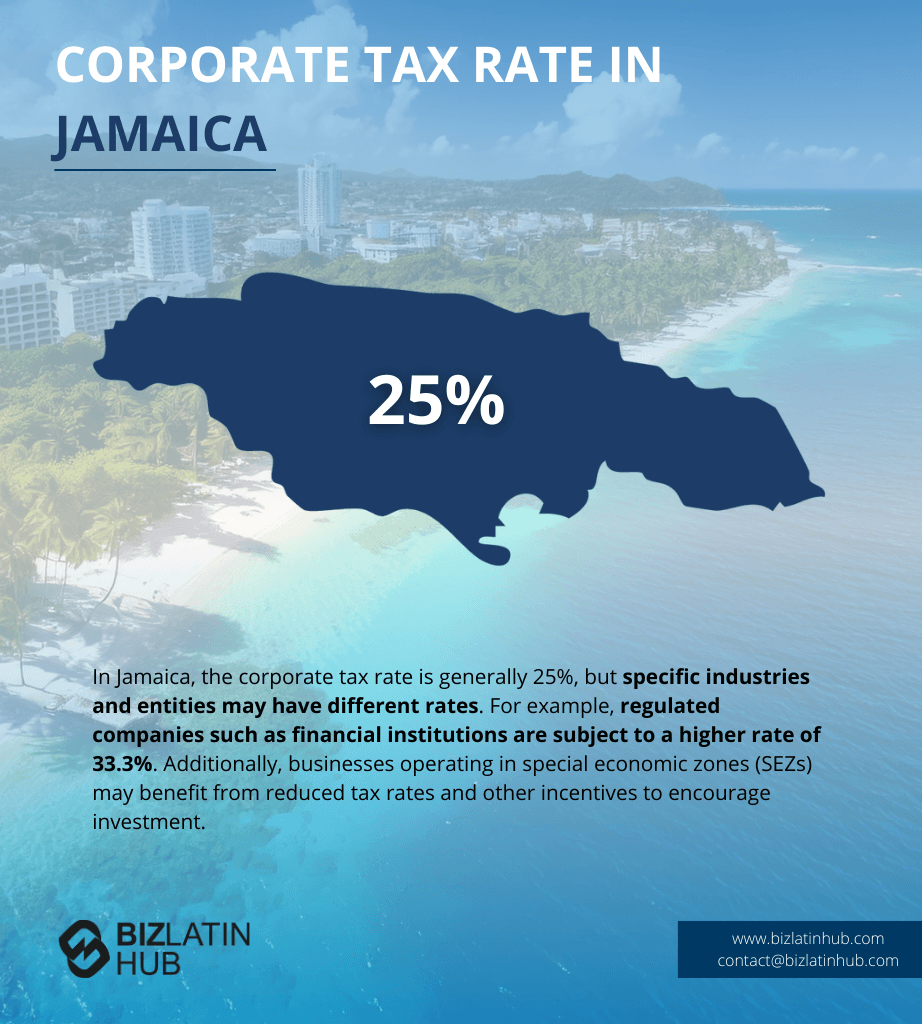
| What Is The Corporate Tax Rate in Jamaica? | Regulated companies governed by entities such as the Bank of Jamaica or the Financial Services Commission, face a 33% CIT rate, with some exceptions |
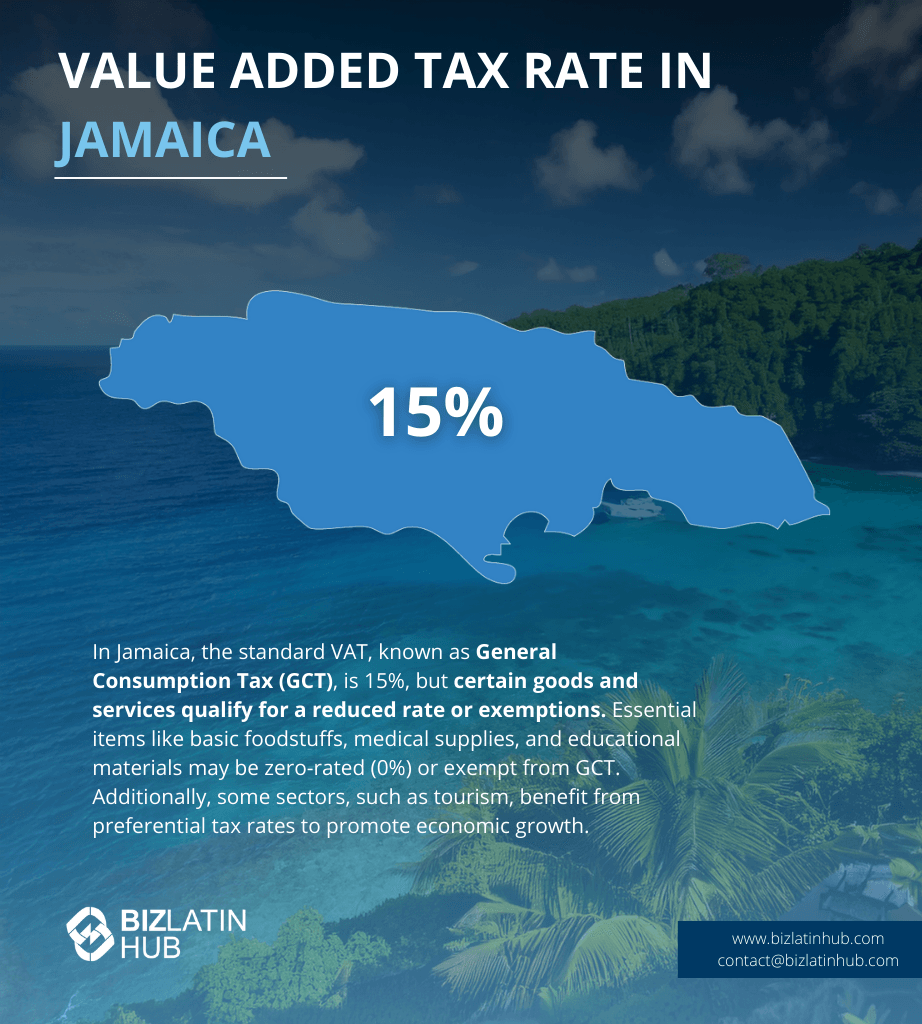
| Jamaican Value Added Tax Rate | The current VAT rate (known locally as GCT) is set at 15%, with a few variations depending on services and business activity. |
| What is The Dividend Tax Rate in Jamaica? | Resident corporations pay a 15% tax rate while non-residents pay a rate of 33%. |
What are the tax rules in Jamaica?
A corporation residing in Jamaica is taxed on its income worldwide, while non-resident companies are taxed only on income generated within Jamaica. Tax, at a rate of 33%, is applied to specific income sources like interest, dividends, royalties, and fees for non-resident corporations. However, if the recipient resides in a country with a double taxation treaty (DTT) with Jamaica, lower withholding rates may apply.
Tax and accounting requirements in Jamaica: Key local tax rates
Understanding the tax and accounting requirements in Jamaica is pivotal when starting a business in this market. Here are the tax rates you need to know.
Income Tax: After considering any applicable tax-free allowances, Most people pay a 25% rate on their earnings, up to 6 million Jamaican dollars per year. If their income exceeds 6 million Jamaican dollars annually, the tax rate increases to 30%.
Corporate Tax: The current corporate income tax (CIT) rates are as follows: Regulated companies governed by entities such as the Bank of Jamaica or the Financial Services Commission, face a 33% CIT rate. Building societies are taxed at 30%, life assurance companies at 25%, and unregulated companies operating within Jamaica at 25%. Specific organizations, such as pension funds and approved charitable organizations, are exempt from income tax as per the approval of the Commissioner General, Tax Administration Jamaica (TAJ).
General Consumption Tax (GCT): The standard GCT rate is 15%, but specific goods and services may have different rates. Telephone services and handsets face a 25% GCT, while hotels and tourism-related businesses pay an effective rate of around 10%.
Asset Tax: A 0.125% asset tax is applied to the ‘taxable value’ of assets belonging to deposit-taking institutions regulated by the Bank of Jamaica, as well as securities dealers, life assurance companies, and property and casualty insurance companies regulated by the Financial Services Commission.
Withholding Tax: Resident corporations pay a 15% tax rate while non-residents pay a rate of 33%.
Social Security: Employers must deduct and remit the specified contributions, along with Pay-As-You-Earn (PAYE) Income Tax for employees, by the 14th day of the following month.
Property Tax: In Jamaica, Property tax is assessed based on different value bands, with rates varying from 0.50% to 0.90%.
Jamaica’s international tax treaties
Jamaica maintains a Bilateral Investment Treaty with the United States and has signed various double taxation agreements with countries such as Canada, China, France, Germany, and the United Kingdom. While not having a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the United States, CARICOM inked a Trade and Investment Framework (TIFA) in 2013.
In 2014, Jamaica and the United States signed an inter-government agreement for reciprocal information sharing under the U.S. Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA).
FAQ regarding tax and accounting requirements in Jamaica
Using our experience, we’ve identified common questions our clients often ask us about accounting and taxes in Jamaica.
Depending on the type of business, the corporate tax rate ranges from 33 to 25%.
A resident corporation is taxable on its worldwide income. Non-resident companies are subject to tax on Jamaican-sourced income.
Tax Administration Jamaica (TAJ) is the name of the revenue authority in Jamaica.
The Institute of Chartered Accountants of Jamaica (ICAJ) holds the authority granted by the Public Accountancy Act as the standard-setter in the jurisdiction. ICAJ has officially embraced and implemented IFRS and IFRS for SMEs as the prevailing accounting standards.
In Jamaica, the ACCA (Association of Chartered Certified Accountants) is widely considered the primary professional qualification for local accountants. Nevertheless, individuals with the CPA (Certified Public Accountant qualification) from the United States of America continue to enjoy high esteem among employers.
Jamaica does not place restrictions on foreign ownership or control, and local laws treat investors, whether local or foreign, without distinction.
Biz Latin Hub can help you with tax and accounting requirements in Jamaica
At Biz Latin Hub, we provide an extensive range of market entry and back-office solutions in Latin America and the Caribbean.
Our team has expertise in tax and accounting requirements in Jamaica, with legal services, accounting and taxation, hiring, and visa processing available.
We have strong connections in the LATAM region through solid partnerships. This wide network gives us many resources to help with global projects and explore new markets in different countries.
Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you achieve your business goals in Latin America and the Caribbean.
If this article about tax and accounting requirements in Jamaica interests you, check out the rest of our coverage of the region. Or read about our team and expert authors.