Tax and accounting requirements in Chile should be a key component of your market entry strategy when looking to successfully register a company in Chile. This guide offers essential insights to help you navigate Chile’s fiscal regulations effectively and remain compliant. This is mainly done digitally in Chile. SII (Servicio de Impuestos Internos) manages tax filings, including VAT and income tax. For payroll tax and social contributions you will need to use the online platform known as Previred.
Key Takeaways Tax and Accounting Requirements in Chile
| What Are The Accounting Standards in Chile? | The IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standard) The official accounting regulation body is the Chilean Ministry of Finance. |
| What Is The Corporate Tax Rate in Chile? | For SMEs the corporate tax rate in Chile is 25%, for large companies it is 27%. |
| What Is The Chilean Value Added Tax Rate? | The current VAT rate (IVA) is set at 19%, with a few variations depending on services and business activity. |
| Dividend Tax Rate in Chile | Dividend distributions from Chile are subject to a 35% withholding tax. The full amount of corporate income tax paid by the Chilean company (currently 27%) can be credited against this tax. |
Overview of the Chilean Accounting and Tax System
In Chile, companies must follow IFRS or IFRS for SMEs depending on size. Mandatory books include the Libro Diario, Mayor, Balance, and Libro de Remuneraciones. Electronic invoicing (Factura Electrónica) is mandatory and must be issued through the SII portal or certified providers, in line with the general requirement for financial information to be digitised. Chile’s accounting standards are:
- The IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standard)
- The official accounting regulation body is the Chilean Ministry of Finance.
Basic financial statements must include:
- A statement of financial position
- A statement of comprehensive income
- A statement of cash flows
- A statement of changes in shareholder equity
- Notes to the financial statement.
Additionally:
- The legally recognized currency is the Chilean Peso.
- Concerning accounting laws, all laws registered are defined by the Codigo Tributario.
- The tax year starts on the 1st of January and ends on 31st of December in the same year.
- Local accounting for companies in a foreign currency (USD, EUR) is allowed but needs to be specifically authorized and cannot be changed for two years.
What is a Chilean taxation number?
When carrying out business in Chile a company has to be registered and obtain a Chilean taxation number and tax ID (RUT). When a company’s deals with the country’s taxation, this number is required in order to deal with the national tax authorities. Moreover, every individual, including foreign individuals in Chile must obtain a Chilean National Tax ID and a password for the Chilean IRS website in order to be able to file their annual tax returns.
Who pays tax in Chile?
Taxpayers in Chile are companies, individuals and other legal entities, affecting the income of all corporations and individuals. All individuals and companies are subject to an income tax on their monthly or annual income. Foreign individuals pay income tax only on their Chilean income during their first three years in the country. This period can be extended for three more years, although after that they are also subject to income tax on worldwide income.

The tax authority in Chile is the Internal Revenue Service (SII – Servicio de Impuestos Internos) which is a public organization and depends on government administration in Santiago, Chile. From the time the taxpayer filed the return, the tax authority (SII) has an official three-year time limit in order to review, amend or rectify any tax return previously filed.
VAT stands at 19%, more or less in line with similar economies in the region. Import and export taxes, as well as customs, is a more complex area, but the country has signed a large number of Free Trade Agreements, meaning that a great deal of goods and services are exempted from tariffs and trade barriers.
Corporate Income Tax, VAT, and Monthly Filings
The Chilean income tax system affects business income, salaries, other personal income, as well as income which was obtained by non-residents. Income-tax is structured in different categories and they have to be applied accordingly. Categories are First Category, Second Category, Complimentary Global and Additional taxes.
Generally in Chile, two main tax rates have to be taken into account, the first is the tax rate for companies or corporate tax (first category tax), where income is received by exercising commercial, industrial, agricultural and other activities and the second important tax is the tax on employment income (second category tax). Also, for companies there is the Semi-Integrated Regime (27% rate) and the Pro-Pyme Regime (15–25%) for small companies.
Chile’s First Category Tax (Corporation Tax)

All companies which are resident and domiciled in Chile are subject to “First Category Tax” (FCT) and are taxed on their worldwide income. All company’s non-resident in Chile are taxed on their income received in Chile only. The first category tax is calculated on the basis of the company’s taxable profits generated within a tax year.
Additionally, all companies based and operating in Chile are required by law to make monthly advance payments (PPM), through monthly declaration (F29), and there is also a non-obligatory voluntary (PPM) for companies who wish to keep an additional provision for the yearly income tax, and in the case of an overpayment the Internal Revenue Service makes a refund of the exceeded amount.
The first thing the taxpayer must know is the tax regime to which it is subject, which determines its tax obligations, such as the filing of certain tax returns. The taxpayer can consult their current Tax Regime or that of previous periods in their personal MiSII section by selecting the option Personal and Tax Data and then Taxpayer Characteristics.
Chile’s Second Category Tax (Personal Income Tax)
The Chilean income tax law is described in detail in the Decree Law 824 of 1974 and is administered by the Chilean Internal Revenue Service’s (Servicio de Impuestos Internos). In general, it can be said that every person working and living in Chile, resident or nonresident, is subject to Chilean income tax. All entities resident or domiciled in Chile are taxed on their worldwide income. Non-residents are only taxed on their income earned in Chile.
Therefore, the Second Category Tax is concerned with all personal sources of income including salaries, bonuses, gratuities and other forms of remuneration. The highest progressive rate for this tax is 40% and all taxes have to be paid on a monthly basis in accordance with a monthly timetable issued by the Chilean Tax Authority (Servicio de Impuestos Internos).
This tax is deducted from the gross salary by the employer and subsequently paid over to the Chilean Internal Revenue Service. Depending on the type of income 6 different income tax rates apply. Furthermore, the income tax is based on the following two factors:
- The taxpayer’s place of residence
- Source of the income
The taxpayer’s place of residence: In order to be considered to be a resident, a person has to have lived more than 6 months within a calendar year in Chile. For non-residents and non-domiciled, the tax rate is 15% if the activities are technical or professional services if they are not a tax rate of 35% has to be paid on their Chilean-source income alone.
Source of the income: Income is to be considered Chilean source income, when the income is received while performing activities within the country, as of services for businesses and income from property, dividends, royalty and other income. Therefore, the income is sourced where the service is provided.

Value-added tax and accounting requirements Chile
Value-added tax in Chile has to be paid on all sales and imports of goods and services. Furthermore, additional taxes and import duties have to be applied when importing certain goods such as beverages, jewels, and others. Currently, the VAT rate is set at 19% of the price of the goods or services. With regards to importing, the taxable basis is the customs value, CIF Value, which has to be considered and already includes customs duties. VAT returns must be filed on a monthly basis.
Regarding exports of goods and services, the VAT rate is zero, not considering how the product will be exported. Additionally, as of January 1, 2023 all services (with few exceptions) are taxed with VAT.
According to the Law, the following services will not pay VAT:
- Passenger Transportation (Urban, interurban, interprovincial and rural).
- Education (Schools, Kindergartens, Universities, among others).
- Outpatient health services (medical and dental consultations, psychologists, psychiatrists, kinesiologists, imaging, among others).
- Other services that were already exempted in the VAT Law, such as:
- Tickets to shows (*)
- Lease of unfurnished real estate
- Others (Sales and Services Tax Law Art.12 and 13).
- All other exemptions contained in the VAT Law and other legal texts remain in force.
Accounting Standards and SII Reporting Obligations
When tax returns are not filed within the timetable established by the tax authorities or if they contain errors, fines have to be paid. The amount of the fine depends on the length of the debt due and the channel of payment the taxpayer uses to pay the debt. Usually, the amount is three times the tax, then the tax initially due, but when using the SII online payment the percentage of the fine is lower than when paying at one of the offices directly.
When paying these penalties, the Internal Revenue Service (SII) has a policy known as Condonacion in which if you pay the total amount of the debt, is up to a discount of 70% of legal fees (interest and fines), this a benefit of the new tax reform.
The tax system in Chile is very flexible if everything is always properly informed, even when in debt; it supports businesses to keep on growing, through payment facilities. Monthly VAT and payroll filings must be made by the 12th of each month. Annual corporate tax (Form 22) in done in April and the annual sworn affidavits (DJ): March.
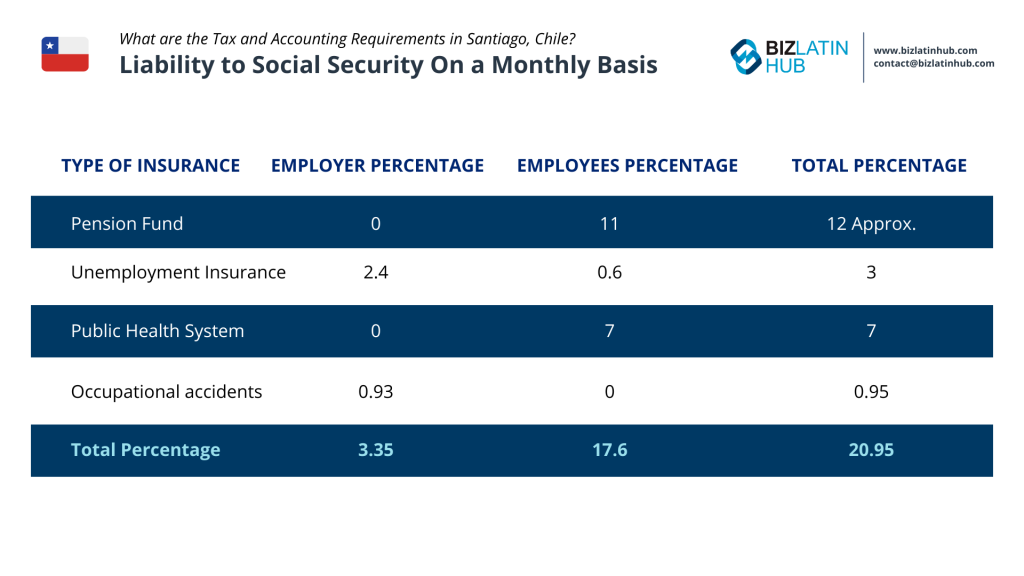
In general, it can be said that social security deductions make up to 20% off the monthly salary, these contributions include payments into the pension fund, the health insurance, unemployment insurance and the Chilean association of security. Employers must contribute to: AFP (pension), Fonasa/Isapre (health), AFC (unemployment), mutual de seguridad (accidents). Monthly filings must be made via Previred.
Health contributions
Chile’s health system has existed since the 1950’s, it was originally introduced as a national health care system and was one of the first in Latin America. The relevant agency for the health care system is the Fondo Nacional de Salud (FONASA). Today workers can choose between the private health system Instituciones de Salud Previsional (ISAPRE) and the public health system Fonasa. The monthly mandatory payment is 7% of monthly income for FONASA and about 9.2% for the private system ISAPRE.
Pension fund contributions
Regarding the pension system, all employees can choose between six different private pension companies and furthermore are able to choose between different types of funds. The monthly mandatory payment on their income is approximately 12%. Any individual can pay a higher percentage if they decide to. If workers are self-employed they can decide whether to contribute or not and which amount they want to contribute on a monthly basis.
| AFP | OBLIGATORY RATES (AFP) | ||
| DEPENDENT | INDEPENDENT | ||
| % | SIS (1) (2) | AFP RATE (3) | |
| Capital | 11,44% | 1,88% | 13,32% |
| Cuprum | 11,44% | 1,88% | 13,32% |
| Habitat | 11,27% | 1,88% | 13,15% |
| PlanVital | 11,16% | 1,88% | 13,04% |
| ProVida | 11,45% | 1,88% | 13,33% |
| Modelo | 10,58% | 1,88% | 12,46% |
| Uno | 10.69% |
(AFP): Pension Fund Contributions
(SIS): Disability and Survival Insurance
1) Employer payment.
2) SIS doesn’t apply for pensioner dependent employee.
3) This rate includes SIS, which corresponds to the employee.
FAQs About Tax and Accounting in Chile
Based on our extensive experience these are the common questions and doubts from our clients when looking to understand accounting and taxation in Chile.
1. What is the corporate tax rate in Chile?
A1: The general corporate income tax rate is 27% under the Semi-Integrated Regime. SMEs may opt for the Pro-Pyme Regime with lower rates (15–25%).
2. How are businesses taxed in Chile?
In Chile, as far as business is concerned, taxation is based on income actually received.
3. What is the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Called in Chile?
The IRS in Chile is called el Servicio de Impuestos Internos or in English, The Tax Administration Service, and is responsible for implementing the fiscal and customs legislation in Chile.
4. What is the accounting standard in Chile?
Chilean accounting standards require companies to prepare their financial statements in Spanish and according to Normas Internacionales de información financiera (NIIF) or in English, IFRS and Principios de la Contabilidad Generalmente Aceptados. (PCGA).
5. What is the CPA equivalent in Chile?
The equivalent of a CPA in Chile is a Colegio de Contadores AG certified public accountant (Contador Publico Certificado—CPC).
6. Does Chile report in IFRS?
In general terms, and as far as all BLH clients in Chile are concerned, according to the current regulations, since 2009 all companies must follow the IFRS standards.
7. What is the VAT rate in Chile?
The standard VAT (IVA) rate is 19%, with monthly filings required through the SII (Servicio de Impuestos Internos).
8. What payroll taxes are required in Chile?
Employers contribute approximately 25% of gross salary to pension, health, unemployment, and labor accident insurance funds. Contributions are filed monthly via Previred.
9. What are the bookkeeping requirements in Chile?
All companies must maintain electronic accounting records and submit monthly and annual declarations to the SII. IFRS is mandatory for medium and large companies.
10. When are tax returns filed in Chile?
Monthly VAT and payroll returns are due by the 12th of each month. Annual corporate income tax declarations are submitted in April via Form 22.
Why Invest in Chile?

Now is an excellent time to invest in Chile, given its economic stability, strong institutional framework, and rich natural resources.
Chile is the world’s largest copper producer and a major player in lithium production, essential for renewable energy and technology industries.
Opportunities are also growing in renewable energy, agriculture, and technology, supported by the country’s commitment to innovation and sustainability.
Chile’s open economy and extensive network of free trade agreements make it a strategic hub for global business. Ongoing infrastructure development and investment-friendly policies, including simplified regulations and incentives for foreign capital, enhance its appeal.
With a skilled workforce and access to regional and international markets, Chile presents a promising environment for businesses and investors.
Biz Latin Hub can help you comply with accounting requirements in Chile
If you want to start a company in Chile, it is advisable that you have the support of a qualified account and tax specialist from the start. A well thought out business plan will not be able to evolve if your business does not remain compliant with the various accounting requirements in Chile.
Biz Latin Hub can assist you with all accounting, taxation and financial matters. Our specialist team have a comprehensive understanding of the accounting requirements in Chile and are well equipped to work with foreign companies looking to conduct commercial activity in the region.
To learn more about the Chilean economy, the business opportunities to form a company in Chile, and how you might take advantage of these political shifts, please contact us today. Or read about our team and expert authors. Interested in hiring local staff in Latin America?
See how we can support through either local company formation or through a tailored PEO solution.