An entity health check reviews your company’s compliance with Ecuador’s laws. This review covers all legal requirements for businesses operating in Ecuador. Companies need regular health checks to avoid penalties and maintain legal status.
Key Takeaways: Entity Health Check in Ecuador
| Topic | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Main compliance areas | Corporate structure, tax obligations, employment law, data protection (LOPDP), licenses and permits |
| Critical deadlines | March 31 (shareholder meetings), April 30 (financial filings), 15 days (data requests) |
| Who needs health checks | All companies in Ecuador, especially those with assets over USD 1,000,000, foreign subsidiaries, M&A participants |
| Frequency recommended | Annual reviews for most companies, quarterly for high-risk sectors (oil, gas, banking) |
| Common violations | Missed filing deadlines, outdated registered addresses, incomplete IESS registrations, LOPDP non-compliance |
| Cost-saving tip | Combine health checks with annual compliance tasks to reduce fees by up to 30% |
What Is an Entity Health Check?
An entity health check examines your company’s legal compliance in Ecuador. The process reviews corporate documents, tax filings, employment records, and regulatory permits. Companies use health checks to find compliance gaps before authorities discover them.
Entity health checks differ from transaction due diligence. Health checks monitor ongoing compliance for all businesses. Due diligence focuses on specific events like mergers or acquisitions. Both processes help companies meet legal requirements in Ecuador.
Key Compliance Areas in Ecuador
Corporate Structure Requirements
Every company in Ecuador needs a registered office address. This address receives all government correspondence. Companies must update this address when they move locations.
Companies must maintain accurate shareholder records. Board appointments require proper documentation. Legal representatives need valid powers of attorney. These documents prove your company’s legal structure to authorities.
Tax Obligations and Deadlines
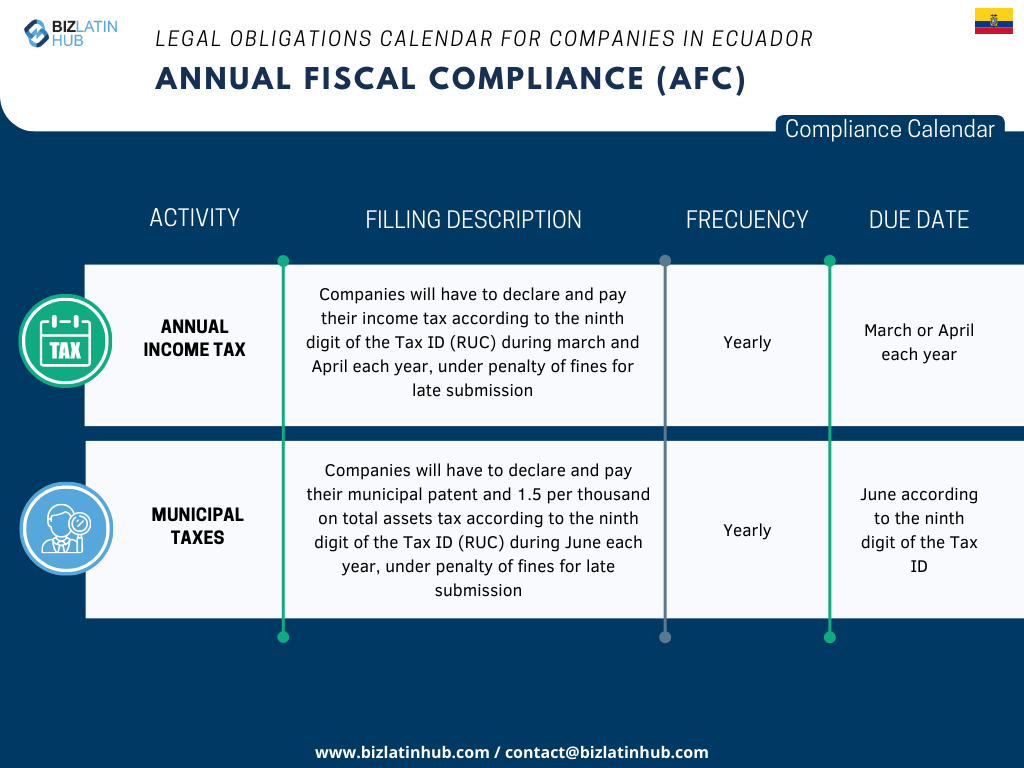
Ecuador requires companies to file taxes on strict schedules. Your RUC tax identification connects to all tax obligations. Companies file VAT returns monthly and income tax returns annually. Municipal taxes vary by city and business type.
Companies must hold shareholder meetings by March 31 each year. Shareholders approve financial statements at these meetings. Companies then submit required documents to authorities by April 30.
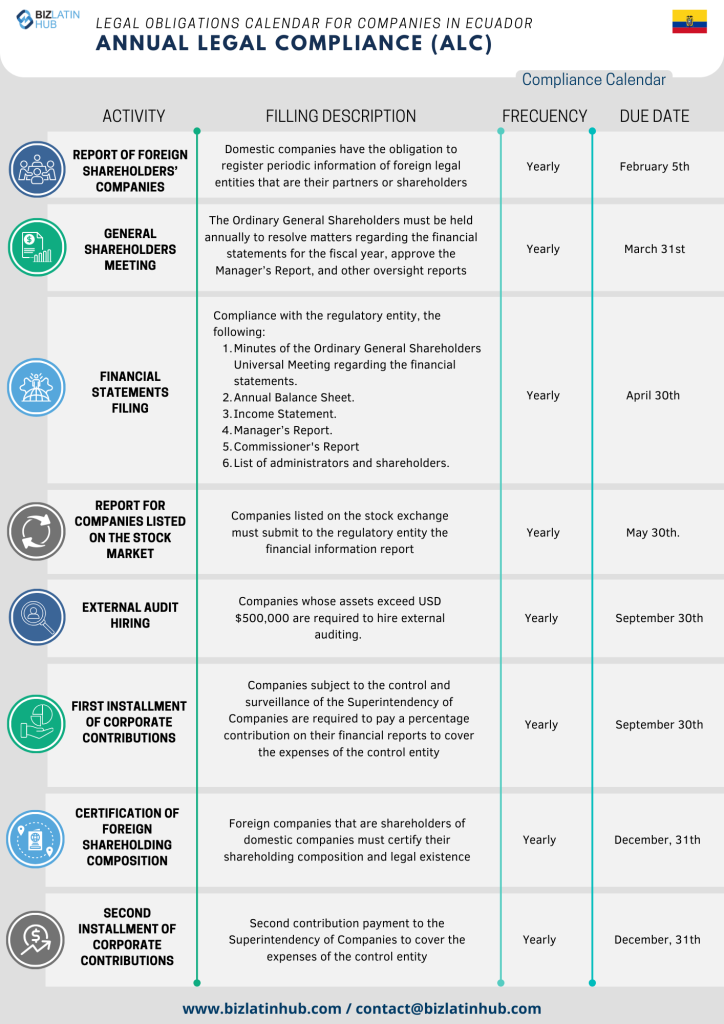
Annual Filing Requirements
| Deadline | Required Action |
|---|---|
| March 31 | Hold shareholder meeting |
| April 30 | Submit financial documents |
Companies with assets over USD 1,000,000 must hire external auditors. Foreign branches need auditors if assets exceed USD 100,000. Oil, gas, and banking companies face additional audit requirements.
Employment Law Compliance
All employees must register with IESS social security before starting work. Employment contracts must include specific clauses required by law. Companies distribute 15% of annual profits to employees through mandatory profit sharing.
Foreign employees need proper work visas. Companies sponsor these visas and maintain immigration compliance. Workplace safety regulations require regular inspections and documentation.
Data Protection Rules
Ecuador’s data protection law (LOPDP) started on May 26, 2021. Companies had until May 2023 to implement required changes. The law gives people control over their personal data.
Companies must respond to data requests within 15 days. Each company needs a designated data protection officer. Risk assessments help identify data security needs. Companies create policies for collecting, storing, and deleting personal information.
Licenses and Permits
Operating permits come from municipal authorities. Each industry has specific license requirements. Environmental permits apply to certain business activities. Import and export businesses need additional authorizations.
The Health Check Process
Week 1: Document Collection
The health check starts with gathering corporate documents. Reviewers examine bylaws, shareholder agreements, and board resolutions. Financial statements show tax compliance history. Permit records confirm regulatory approvals.
Week 2: Gap Identification
Reviewers compare your documents against legal requirements. Missing filings become immediately apparent. Expired permits need renewal. Outdated corporate records require updates.
Week 3: Action Planning
The review team creates a fix-it list with specific deadlines. Each item shows who must complete it and when. Cost estimates help budget for compliance improvements. The plan prioritizes high-risk items first.
Week 4: Implementation Support
Companies receive help preparing required documents. The team assists with government filings. Progress reports track completion of each requirement. Ongoing support continues until full compliance.
Digital Requirements for Modern Businesses
All companies must use electronic invoicing systems. These systems connect directly to tax authorities. Digital signatures replace physical signatures for official documents. Companies processing data need cybersecurity measures.
E-commerce businesses follow consumer protection rules. Websites must show clear prices and return policies. Payment systems need security certifications. Customer data requires special protection.
International Transaction Rules
Transactions over USD 5,000 require Central Bank reports. Companies document transfer pricing for related-party deals. Anti-money laundering rules apply to all businesses. Foreign exchange regulations affect international payments.
Industry-Specific Requirements
Financial services companies follow strict anti-money laundering rules. Oil and gas operations need environmental impact assessments. Technology firms protect intellectual property and user data. Manufacturers document import procedures and quality standards. Service providers obtain professional licenses.
Food and pharmaceutical companies need ARCSA registrations. Product labels must meet INEN standards. Advertising follows strict content rules. These sectors require specialized compliance knowledge.
Common Compliance Mistakes
Many companies miss the March 31 shareholder meeting deadline. Starting preparations in February prevents this problem. Document gathering for April filings should begin in January.
Companies often forget to update their registered address after moving. This causes missed government notices. The 15-day data request response requirement catches many companies unprepared.
Foreign companies sometimes apply compliance rules from other countries. Ecuador has unique requirements that differ from neighbors like Colombia or Chile. Local knowledge prevents these errors.
Building Your Compliance System
Successful compliance requires regular monitoring. Companies assign specific people to track deadlines. Document management systems organize important records. Regular reviews catch problems early.
Combining annual compliance tasks saves money. Companies can reduce professional fees by coordinating health checks with regular filings. This approach eliminates duplicate work.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should we conduct an entity health check in Ecuador?
Annual comprehensive reviews are best practice, with quarterly compliance checks advisable for high-risk sectors such as oil, gas and banking, or for companies holding assets above USD $1,000,000.
What’s the difference between due diligence and an entity health check?
Due diligence in Ecuador is usually a one-off, pre-transaction investigation (e.g., before an acquisition), whereas an entity health check is an ongoing compliance review ensuring the company remains in good standing. Both serve different stages of the business life cycle and are complementary.
What are the penalties for non-compliance in Ecuador?
Data protection breaches: fines up to 1% of annual revenue.
Late tax filings: 3% monthly interest plus statutory fines.
Failure to hold shareholder meetings: warnings that can escalate to dissolution proceedings if unremedied.
Can foreign companies conduct their own Ecuador entity verification?
Technically, yes, but frequent regulatory changes and province-level variations make local legal counsel indispensable. Engaging Ecuadorian professionals minimizes interpretation errors and accelerates approvals.
How long does a complete entity health check take?
A standard engagement lasts 2–4 weeks, depending on corporate complexity and document readiness. Expedited (“rush”) services are available, especially when the review forms part of an M&A due-diligence timeline.
Take Action Now
Regular health checks prevent compliance problems. Early detection of issues saves money and protects your business. Professional reviews identify hidden risks in Ecuador’s regulatory system.
Entity health check services include full compliance audits, risk identification, deadline tracking systems, and local representation. Digital compliance support helps modernize your operations. Industry experts guide sector-specific requirements.
Professional compliance services provide accurate assessments. Local experts know current regulations and coming changes. Ongoing support maintains compliance as your business grows.
Contact compliance specialists to schedule your entity health check. Protect your business with regular compliance monitoring. Start your assessment today to ensure full legal compliance in Ecuador.





