Considering tax and accounting in Ecuador should be a core component of your market entry strategy to register a company in Ecuador and maintain compliance with its intricate regulatory framework. This guide provides key details to help you navigate Ecuador’s fiscal obligations efficiently with the relevant bodies. The SRI (Servicio de Rentas Internas) handles tax filings and IESS (Instituto Ecuatoriano de Seguridad Social) oversees social security.
Key takeaways on tax and accounting in Ecuador
| What Are The Accounting Standards in Ecuador? | Ecuador’s accounting standards mandate financial statements and records in Spanish, following PCGA or NIIF principles. |
| What Is The Corporate Tax Rate in Ecuador? | Costa Rica’s tax rate varies depending on annual revenue, 30% is for companies with gross income over CRC 122,145,000. |
| What is The Ecuadorian Value Added Tax Rate? | The current VAT rate (IVA) is set at 15% in Ecuador. |
| Dividend Tax Rate in Ecuador | Ecuadorian companies owned by residents or non-residents from non-tax-haven jurisdictions are taxed at a rate of 22% or 25%. |
Overview of Ecuador’s Tax and Accounting System
The Ecuadorian tax system is friendly for foreigners since they are only taxed on income earned within Ecuador. Large companies in the country must use electronic accounting. Required books are the Diario, Mayor, Inventario y Balances. Annual financial reports should be submitted in XBRL if required.
In Ecuador, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are applied and financial statements must be submitted annually to the Internal Revenue Services and the superintendence of companies. Ecuador has 19 tax treaties and the national tax authority responsible for taxation matters within Ecuador is the Internal Revenue Service (SRI).
The tax authorities have three years from the date of filing to review tax returns and make changes if deemed necessary. If a tax return was filed incomplete or not at all, the period of review can be extended for up to 6 years.
Usually, when an economic activity is carried out in Ecuador, companies as well as individuals, have to register before the national tax authority. Once the national tax identification number has been registered for, the RUC can be obtained.

Corporate Income Tax and VAT in Ecuador
Corporation Tax
All companies that reside in Ecuador, are incorporated in Ecuador, or have operations and a management center in Ecuador are subject to a corporation tax rate of 25-28% on their worldwide income, and have discounts when disabled or senior staff are hired. Companies which are non-resident in Ecuador (all companies not incorporated in Ecuador) only have to pay income on their income sourced within Ecuador.
The end of the Ecuadorian tax year is the 31st of December and taxes must be filed in April, the exact date depends on the 9th digit of the Ecuadorian tax identification number.
Value Added Tax – IVA
The tax from which most income is generated in Ecuador is IVA, which is the Ecuadorian Value Added Tax. Currently, the tax rate for the IVA is 12% and is paid on almost all purchases of goods, imports and the provisions of services. VAT returns must be filed monthly using Form 104, between the 10th and the 28th of the following month of the transaction – the exact day depends on the company’s tax identification number, RUC.

Other Relevant Taxes in Ecuador
Apart from the normal taxes that have to be paid within the country, such as the corporation and value added tax, additional tax rates are applied and therefore have to be taken into account. Additional taxes in Ecuador are taxes on property, capital gains tax, foreign money transfer tax, and others.
Municipal tax on capital gain in the transfer of real estate (Plusvalía)
10% real estate transfer tax applies to the transfer of urban real estate property.
Property Tax
Property taxes in Ecuador depend on the municipal value of the property and the exact tax percentage of the property tax depends on the city in which the property is situated in. A special part exemption applies for this tax which allows owners over the age of 65 years to pay half of the applied property tax rates. In general, it can be mentioned that the property tax rate at the moment ranges from 0.025% to 0.3% for rural property and from 0.025% to 0.5% for urban property.

Income Tax on the occasional sale of real estate
Any person or company that sells its offices, commercial premises or industries, must pay a tax on the difference between the purchase price and the sale price of the property (profit). The rate ranges between 5% and 37% on the capital gain.
This tax will not be applicable for the first sale of a property. That is to say, the tax must be paid from the second sale of offices or commercial premises.”
Foreign Money Transfer Tax (ISD) – Capital Outflow Tax
This tax applies to all monetary transactions and operations which are carried out abroad in a foreign currency. The applied tax rate is 3.5% and has to paid by all foreign and local companies, as well as all individuals and foreign banks when doing monetary transactions.
Incentives
As of 2022, Ecuadorian tax law provides for a three percentage points reduction in the income tax rate for new corporations and investments. The latter will be applicable for up to 15 years. The accumulated exemption may not exceed the amount invested.
SRI Compliance, UBO Declarations, and Electronic Books
As in most other countries, in Ecuador, fines, and penalties have to be paid when taxes are filed late or incorrectly. If a tax return is not filled at all, companies, as well as individuals, are subject to prosecution.
The RUC (Registro Único de Contribuyentes) must be updated annually as well as UBO information via the dedicated SRI system. Penalties apply for non-compliance.
If the tax is paid late, penalties have to be paid for late payment at a fixed rate of 3% of the value of the tax generated, for each month of delay.
In addition, a penalty of USD$30 to USD$60 must be paid for not having declared the tax on the due date.
If taxes have been filed incorrectly, a “substitute form” must be filed as determined by the Internal Revenue Service (SRI) for each year.
In Ecuador, the end of the tax year is the 31st of December. Following the tax year, from the 2nd to the 28th of April, all corporation taxes have to be filed and paid. The exact filing date depends on the taxpayer’s identification number.
Payroll Contributions and IESS Reporting in Ecuador
The employer has to file the monthly income tax for all employees, so employed individuals don’t have to deal with the tax office themselves. As mentioned before, the exact date of filing depends on the 9th digit of the tax identification number. When foreign individuals decide to move to another country they have to make sure to have paid all their income taxes as well as cancel their taxpayer identification number (RUC) if they have received one during their stay.
In Ecuador, there are three different agencies for the social security system; the agencies include IESS for employees and workers employed in the private or public sector, ISSPOL and ISSFA for members of the police and the military. IESS covers health, pension and work risk insurance for all employees and workers. All three systems work independently and do not coordinate with one another.
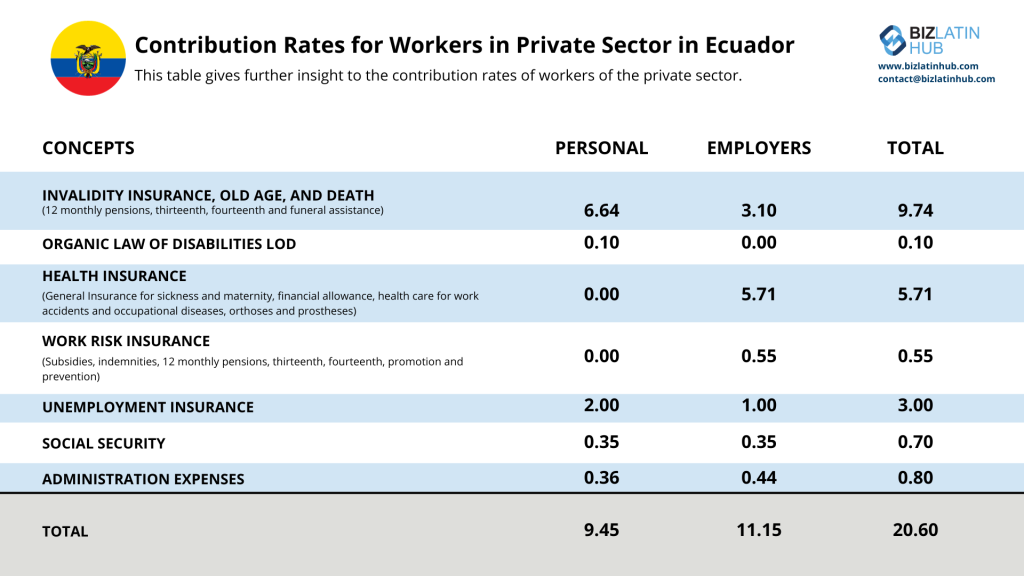
The social security tax for employees will automatically be discounted from their monthly salary, this tax rate is based at 9.45% on their monthly income. The responsible agency for the system is the ministry of social welfare (IESS) – contributions to social security have to be made by both employer and employees.
Generally speaking, all workers and employees have to pay monthly contributions which are deducted from their monthly salary. Additionally, all employers have to make an 12.15 % of the value of the monthly salaries of their workers. This amount is assumed by the employer as they cannot discount it from the salary of the worker.
When an employee reaches the age of 65, a pension can be claimed, as long as they have contributed to social welfare for a minimum of 15 years. When the employee wants to retire early at 55, they have to prove a minimum contribution to the social welfare of 30 years. Regarding maternity, this insurance is covered when the employee has worked at least 360 days before leaving for maternity.
Additionally, all employers have to make additional contributions to the Ecuadorian professional training service (SECAP) and to the Ecuadorian institute of education and educational credit (IECE), each additional contribution is 0.5% of each employee’s salary, but this amount has to be paid by the employer.
Contribution Rates for Workers in Private Sector in Ecuador
FAQs About Accounting and Tax in Ecuador
Based on our extensive experience these are the common questions and doubts from our clients when looking to understand accounting and taxation in Ecuador.
The corporate tax rate in Ecuador is 25%
Taxable income obtained by companies incorporated in Ecuador, as well as by branches of foreign companies domiciled, will be taxed at a rate of 25% of their taxable income, which works based on paying tax on the difference between revenue minus deductible expenses.
The IRS in Ecuador is called the Servicio de Rentas Internas (SRI) and is responsible for administering the country’s tax collection and executing fiscal policy.
Ecuador’s accounting standards require companies to prepare their financial statements in Spanish and according to the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles or PCGA or NIIF. Accounting registries and books of account must be recorded in Spanish.
The equivalent of a CPA in Ecuador is a Certified Public Accountant registered at the Association of Public Accountants of Ecuador.
All listed companies must follow IFRS Standards including financial institutions and insurance companies.
VAT is 12%, with reduced rates of 0% for certain basic goods. Filed monthly with the SRI.
Yes. Employers contribute ~12.15% to IESS (health, pensions, work risk), while employees contribute 9.45%.
Companies must register their Ultimate Beneficial Owners (UBOs) with the SRI annually or when changes occur.
Libro Diario, Libro Mayor, and financial statements are required. Large taxpayers must use electronic accounting (PLE).
Why Invest in Ecuador?

Ecuador is a land of untapped potential, offering a stable, dollarized economy and a prime location at the crossroads of South America. With well-developed infrastructure connecting global markets, the country is positioned as a strategic gateway for trade.
Rich in natural resources, ranging from oil and minerals to high-value agricultural products, Ecuador is diversifying its economy through business-friendly policies, tax incentives, and new opportunities in tourism, agribusiness, and manufacturing. These measures have created an environment where investment and innovation thrive.
Beyond its economic advantages, Ecuador stands out for its affordability, skilled workforce, and unparalleled biodiversity, making it a hotspot for eco-tourism and green projects. Its vibrant export sector, driven by products like bananas, shrimp, and roses, ensures steady growth and resilience.
Ecuador’s increasing focus on renewable energy and technology underscores its forward-thinking approach, offering investors the chance to contribute to a sustainable and globally connected future.
Biz Latin Hub can help with tax and accounting requirements in Ecuador
Understanding taxation and accounting requirements in Ecuador will make it easier for you to budget. Additionally, it will help you understand what you will have to deal with when it’s time to declare your taxes.
If you would like more information about accounting regulations or tax laws in Bolivia, Biz Latin Hub’s group of experts offer you legal and accounting assistance for your business in Ecuador. Take advantage of our large range of multilingual market entry and back-office business solutions to meet your company’s incorporation and compliance needs.
Contact us now for help in establishing a successful business in Ecuador.
Learn more about our team and expert authors.